Techniques for finding the shortest and the fastest pathways can
be useful during sampling for pathways, in post-processing and
analysis of DPS databases, and in various optimisations of pathway
ensembles
[
,
,
,
,
]. Given a digraph representation of a
connected database of minima and transition states it is possible to identify
the shortest path between any two minima using a breadth-first search
algorithm
[
], which runs in linear time. The shortest path, however, is not
necessarily the fastest. Recently Evans suggested using Dijkstra’s
algorithm
[
] for finding the path with the largest non-recrossing DPS
rate
[
]. It was pointed out by Carr, however, that the weight
function used in Reference
[
] is not positively defined, and the use of
the Bellman-Ford-Moore (BFM) algorithm
[
–
] was suggested
instead
[
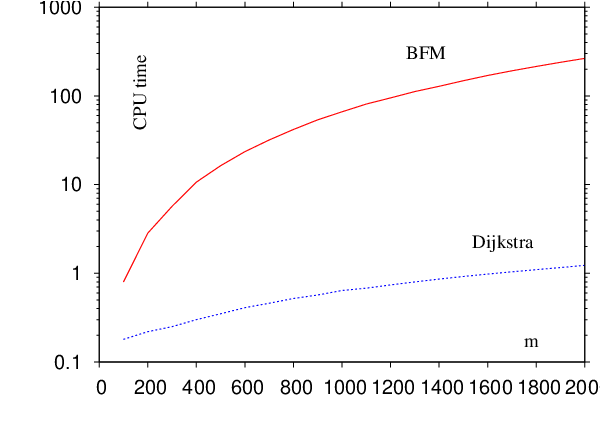
]. Because Dijkstra’s algorithm scales better than BFM
algorithm (see Figure
) we describe below a weight function that
enables us to use the Dijkstra’s algorithm for finding the fastest
path.
As detailed in Section 4.1.1, within a digraph representation of a coarse-grained PES each minimum is represented by a single node and each transition state is represented by two oppositely directed edges. Here we ignore degenerate rearrangements since they do not affect the rates, and for cases where more than one transition state links the same pair of minima only the one with the fastest forward and backward rates is used. Adopting the non-recrossing DPS rate definition from Equation 4.11 we can associate forward and backward rate constants
| (E.1) |
with a pathway .
For a detailed description of Dijkstra and BFM algorithms we refer the reader to Reference [154]. A suitable choice of edge weight function to be used with either of the shortest path algorithms must be made. We define the weight of each directed edge as
| (E.2) |
Note that and . Since the weight is non-negative it is possible to apply Dijkstra’s algorithm to find the fastest pathway [154].
It makes sense to include only minima with more than one connection when searching for the fastest pathway. In our calculations we first iteratively identified a connected subset of minima with the number of connections greater than one, and then run the above algorithm for this subset.
To find the fastest path connecting minima and in the direction it is necessary to solve either a single-source shortest paths problem with minimum chosen as a source, or a single destination shortest paths problem with minimum chosen as the destination. In the latter case all the edges in the graph need to be reversed, which can be accomplished by simply swapping the arguments to the weight function in Equation E.2. This reversal is possible because our graph is a symmetric digraph, i.e. if there is an edge then there is also an edge .
A useful check for correct implementation of this algorithm is to verify that the weight of the shortest path from minimum to minimum , , is related to the rate calculated for that pathway by
| (E.3) |
The BFM algorithm runs in time while Dijkstra’s algorithm as described in Reference [153] scales as [154]. Although both algorithms appear to have similar (quadratic) asymptotic complexity for the case of sparse graphs (e.g. ) the scaling prefactor is smaller for Dijkstra’s algorithm. In addition, for sparse graphs with an implementation of Dijkstra’s algorithm that utilises a priority queue of some sort can improve the asymptotic bounds further. Priority queues based on binary min-heap and Fibonacci heap [276] result in and scaling of the algorithm, respectively [154]. In the present work we have used a priority queue based on Fibonacci heap. A performance comparison of our implementations of BFM and static Dijkstra’s algorithms is shown in Figure E.1. 
Since knowledge of all the pathways on a complicated PES is out of the question a representative sample must be obtained to properly describe the property of interest. It is unclear what is the best strategy of evolving the pathway database if the proper description of kinetics is sought, as sampling techniques may introduce a bias towards pathways of particular type.
In previous DPS studies a set of perturbations was applied to the fastest known path to generate new ones [8–10]. New pathways were constructed from a subset of stationary points featured in the pathway being perturbed, and from these that were found as a result of perturbation. Because building the shortest paths tree with Dijkstra’s algorithm is relatively cheap it is possible to analyse the whole database for the presence of new faster pathways rather than just the subset. Results for an example application are presented in Figure E.2. 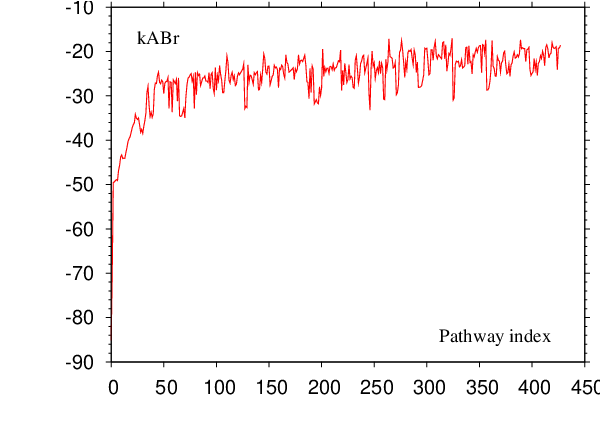
After a set of perturbations was applied to the fastest currently known pathway Dijkstra’s algorithm was used to solve the single-source shortest paths problem to build the shortest paths tree rooted at minimum . For path the set of perturbations constituted attempts to shortcut the path, where is a shortcut parameter, .
Each attempt to shortcut the path was realised as a single connect run (see Chapter 2) seeded with two minima separated by a gap of length along the path. If the fastest path found by Dijkstra’s algorithm was different (not necessarily new) from the one that was currently being perturbed the iteration was completed, this pathway was perturbed in the next iteration and parameter was reset to . Otherwise, was incremented by one, unless in which case the calculation was terminated.